A Bayesian Reformulation of the Drake Framework for Extraterrestrial Probability Estimation
By Kevin L. Brown, Independent Researcher
Published: November 2025
DOI: 10.5281/zenodo.17561254
Introduction: From Speculation to Resonance
The Drake Equation (1961) stood for decades as the foundational conceptual tool for estimating the number of communicative extraterrestrial civilizations ($N$). While brilliant, its reliance on unstable single-point estimates made it mathematically fragile, yielding uncertain results that could span nine orders of magnitude.
The Brown–Drake Resonance Equation (BDR) revolutionizes this framework. It replaces deterministic calculation with Bayesian probability, providing credible intervals ($CI_{95\%}$) and dynamic updating as new data emerges. The core concept of “Resonance” refers to the measurable coherence ($\mathcal{R}$) achieved when probabilistic expectations align with empirical data.
This paper transforms the debate over life in the cosmos into a falsifiable, data-assimilative science.
The Core Transformation: Quantifying the Great Filter
The BDR achieves its predictive power by formally integrating the “Great Filter”—the cumulative challenge to civilizational survival—directly into the mathematical framework.
The traditional Drake Equation treated communicative lifetime ($L$) as a single, highly speculative variable. The BDR decomposes $L$ into conditional survival probabilities that can be constrained by specific lines of research:
| Feature | Classical Drake Equation (1961) | Brown–Drake Resonance Equation (BDR) (2026) |
| Calculation Type | Deterministic Point Estimate | Bayesian Expectation Integral |
| Output | Single value ($N$), no error bounds | Credible Interval ($CI_{95\%}$) for $N_R$ |
| Data Update | Static; requires manual recalculation | Dynamic; automatically updates posterior via Bayes’ theorem |
| Factor $L$ | Single parameter, $L$ (Mean Lifetime) | Conditional Filter Factors ($\tau_c \times P_{\text{INT}} \times P_{\text{EXT}} \times P_{\text{TRANS}}$) |
| Key Metric | Arithmetic value of $N$ | Resonance Index ($\mathcal{R}$) (Coherence between model and data) |
| Prior Treatment | None; all terms assumed certain | Explicit Priors ($\text{Beta}(1,1)$ for speculative terms) |
Conditional Lifetime Factor (L)
The decomposition of L is key to turning conjecture into risk-quantification:
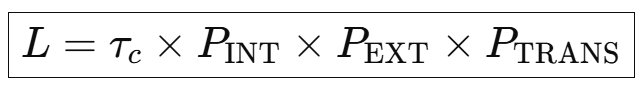

This structure allows Earth-based existential risk research to directly constrain galactic probability.
Bayesian Resonance and Dynamic Updating
The BDR introduces the Resonance Index {R}:
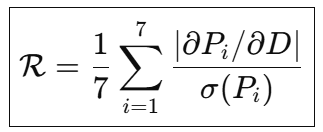

Why It Matters
- Risk Mitigation: The BDR provides a statistically sound mandate for reducing terrestrial risks because constraining these factors immediately narrows the credible interval for $N_R$.
- Scientific Rigor: It enables astrophysical inquiry to proceed with necessary scientific rigor, acknowledging and quantifying uncertainty rather than ignoring it.
- The Future of SETI: The BDR ensures that the search for extraterrestrial life is always anchored to the latest empirical data, maximizing the efficiency and credibility of the global effort.
The BDR thus transforms the estimation of extraterrestrial civilizations from philosophical musing into a progressively empirical, risk-aware science.
